| ICC Build Settings | |
|---|---|
|
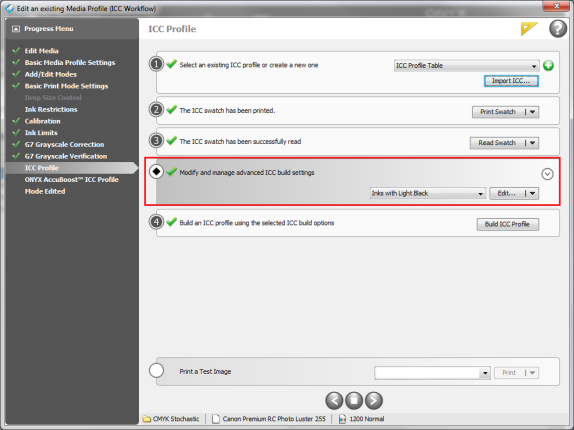
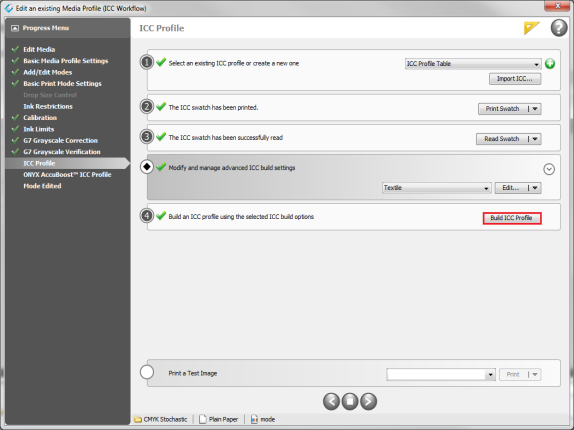
♦ Modify and manage advanced ICC build settings. This option is in the ICC Profile step (Figure 1). Click
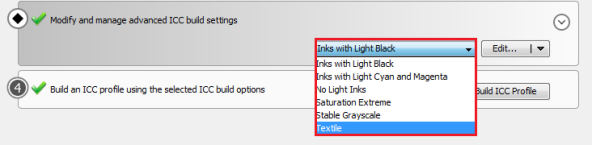
Preset Selection - The drop-down menu contains preset ICC build options. By default Media Manager will auto select an appropriate preset based on the Ink Configuration used in the print mode (Figure 2).
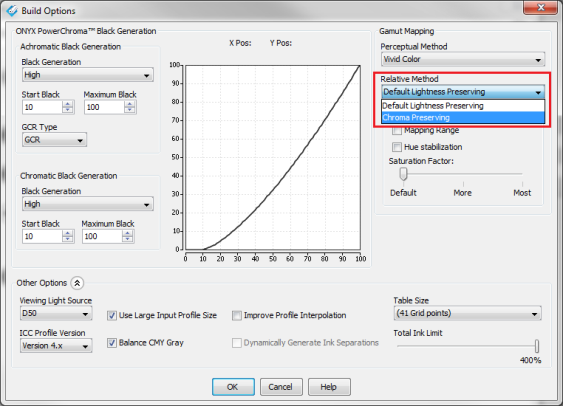
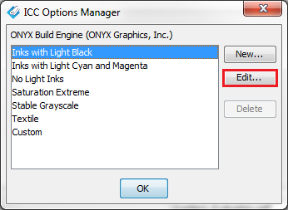
Edit - Clicking this button opens the"ICC Build Options" dialog (Figure 3). Clicking the down arrow opens the “ICC Options Manager” dialog where custom presets can be created. Click [New] to name and configure a custom ICC Build preset (Figure 4).
Achromatic Black Generation (GCR Type: GCR): The [Black Generation], [Start Black], and [Maximum Black] selections control when, how quickly, and to what extent Black ink is used for colors without hue. In other words, these controls affect colors along the general [L*] axis of the profile gamut. An increasing amount of CMY ink will be automatically determined by the profile build engine to achieve the grayscale objectives (from light to dark).
Achromatic Black Generation (GCR Type: GCR Plus): [GCR Plus] is a “smart” black generation option that ensures Lightness values of achromatic grays will decrease smoothly across the range from light to dark. Additionally, ink savings can be achieved by lowering the [End CMY] setting, generally resulting in decreasing CMY ink usage above the entered value. Note that if the desired [End CMY] setting results in a Lightness reversal, [GCR Plus] will try to get as close as possible to the setting while maintaining a uniform decrease in Lightness. The [Black Generation], [Start Black], and [Maximum Black] selections act the same as with the GCR setting.
Achromatic Black Generation (GCR Type: UCR): The [CMY Gray Generation], [Start CMY Gray], and [Maximum CMY Gray] selections control when, how quickly, and to what extent the CMY inks (making up gray) are used to define colors without hue. These controls affect colors along the general [L* ] axis of the profile gamut. An increasing amount of black ink will automatically be determined by the profile build engine to achieve the grayscale objectives (from light to dark).
GCR (Gray Component Replacement): In any two-color combination using C, M, or Y, a two-color combination constitutes a desired color (Chroma). While the third remaining color channel constitutes the Gray Component of the desired two-color combination, and is used to make the color darker. We refer to this third color as the Gray Component. UCR (Under Color Removal): Works a bit differently. UCR defines how much CMY Gray Component to remove when generating black. From a conventional standpoint UCR and GCR are often used in conjunction with one another. You define how much black to use with GCR and how much CMY to remove with UCR. Summary: When using the [GCR] option you are indicating that you want to selectively control the black ink portion. When using the [UCR] option you are indicating that you want to selectively control the Grayscale CMY portion.
NOTE: It is a reasonable assumption that there is a linear increase in the uncontrolled portion of the Grayscale.
Chromatic Black Generation: The [Start Black], [Maximum Black], and [Black Generation] selections control when, how quickly, and to what extent black ink is used for determining dark ink colors at an extreme distances from the [L*] axis. In other words, these controls affect how black ink is used in colorful shadow areas of the gamut.
NOTE: The CGR Type selection is not used for chromatic black generation.
Achromatic: Colors without hue. White, Gray, and Black. Colors along the [L*] axis of the gamut (Luminance). Chromatic: Defined as colors with Hue, or colors along the [a*] and [b*] axis of the gamut (Chroma and Hue).
Any color can be thought of being totally achromatic (having no hue), totally chromatic (a completely saturated color), or a mixture of these two extremes. The Black Generation settings allow for the black generation to be defined for colors at the extremes with a mixing of the black generations being performed when the color is a mixture of the extremes.
To learn more about using Achromatic UCR go to the Thrive article and click the Max-imize tab.
This option determines how out-of-gamut colors are mapped to in-gamut colors. The selected gamut mapping methods only apply when a job is using either the Perceptual or Relative Colorimetric rendering intents.
Perceptual Method – This option gives your output more pleasing, but less accurate color. It adjusts all the colors in the gamut to keep the relationships between in-gamut color and mapped out-of gamut colors the same. There are 4 methods you can select:
Relative Method – This option is especially useful for getting more vibrant spot color reproduction with out-of-gamut colors. In-gamut colors are not adjusted. The selected method will also apply to any type of image data that is processed using the Relative Colorimetric intent. There are 2 methods you can select:
This set of options allows you to set [Mapping Range] and [Hue stabilization].
This option increases the saturation of the calculated ICC values, with chroma increase weighted more than lightness change. The default setting is[ More] for most of the ICC build option presets.
NOTE: For the most significant increase in saturation, it is recommended to also use one of the saturation input profiles.
You can set other legacy and rarely-changed options by clicking the
Viewing Light Source – This option is only available if you use spectral data device to read swatches. It allows you to build an ICC profile for target lighting other than D50. (* Default setting is [D50])
ICC Profile Version - This option allows you to select which version of the ICC Profile standard to use to build the profile. Different versions have different encoding requirements with the ability to address different color management scenarios. For the most compatibility with external color management systems, use the default selection of [Version 4.x]. Using [Version 5.x] may provide finer interpolation sampling of grayscale images as well as support for spectral capabilities in products that make use of extended Version 5 profile workflow scenarios.
Use Large Input Profile Size] - Enabling this option makes your ICC profile suitable for proofing.
Balance CMY Gray - This option uses a legacy method to balance CMY gray values. For best results, this option should be left disabled.
Improve Profile Interpolation- Enabling this option can improve gamut boundary mapping by interpolating data points. However, using this option can cause non-linearities in gamut mapping. It is recommended to use Mapping Range with a value of 0.00, as this will do a better job of finding the gamut boundary. Note that Mapping Range and Improve Profile Interpolation are exclusive to each other, and cannot be enabled at the same time.
Dynamically Generate Ink Separations - This option is only available when using spot channels. It allows for maximum Chroma when using HiFi inks. Disabling this option leaves ink separations static.
Table Size - This option impact the accuracy and size of the ICC Profile. A larger table size (41 grid points) is more accurate but slightly slower than the Standard table size (33 grid points). [41 grid points] is the default setting.
Total Ink Limit - The [Total Ink Limit] sets the maximum percentage of total ink allowed for the profile. 300% means that C, M, Y, and K channels may not all be used together in full capacity (each channel at 100% equals 300%). If you must limit the total ink, you should try adding an Ink Limit calibration before reducing the Total Ink Limit of the ICC Profile itself. The default setting for an ICC Profile is the maximum ink percentage for all of the process channels in the mode.
Click [Build ICC Profile] button after you have read in your swatch and set your desired options. TIP: To learn about Rebuilding ICC Profiles click here. |
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5 |
 icon. You will see Preset Selection and [Edit…]buttons (Figure 1).
icon. You will see Preset Selection and [Edit…]buttons (Figure 1).